How to Calculate ROI in Automation Testing?
ROI Calculator For Test Automation:
ROI, which is also known as the returns on investments, is a metric to determine the effectiveness of an investment. In this instance, we'll talk about the automation of tests. At the moment the competition is becoming stronger. To remain competitive numerous businesses are trying to get the job done in less time and expense. This goal can be achieved through the automation of test scenarios. Although automation testing will incur a higher than the initial investment, the expense will decrease as the process develops.
ROI test automation or Automation testing offers a number many advantages over manually testing. It's not essential in order to completely automate the process. Automation testing is helpful to test regression scenarios. This is due to the fact that when performing regression testing testers must be working with large datasets. Automated testing ROI assists in determining whether the switch to automation is worthwhile. Think about the time needed to set up and test the test using manual labor. Then, compare it to the time required to create the same test using the aid of an automated tool. In the end, verify the return on investment in both cases.
Does your company plan to get started on a new initiative? It is likely that you are thinking of automatizing your work. When you do you may be confused about whether the automation you implement will benefit your business over the long term. In this article, we'll discuss how to determine ROI prior to making the decision to implement automated testing. We'll go over the importance of making calculations for ROI and the process of calculation as well as some of the most advanced methods and best practices to make these calculations.
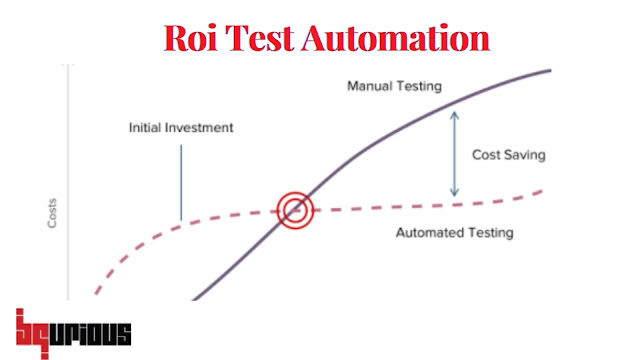
How do you calculate the ROI of test automation:
The most simple method of the calculation of test automation ROI is using the formula below:
ROI = Savings / Investment
Savings: The amount saved when replacing manual tests with automated tests.
Investment: The money is funneled into the creation of automated test pipelines.
ROI could refer to any amount of savings or investment type, it is a reference to time or money.
Savings
Savings is the difference between the cost of conducting tests manually versus automatizing the same tests at a certain amount of times during a particular time. In simpler terms:
Cost savings = (time to conduct an individual test manual - time required to run the same test using automated) A the number of tests number tests
Source
In the formula above, the number of tests is to be an average over the period of time specified. In addition, if tests run quicker, you'll have a more likely chance of getting a positive ROI.
Investment
The term "investment" refers to the entire amount of ongoing and fixed costs associated with test automation. This is the amount of time and money that is spent setting up and setting up the automation framework, along with the time and effort to write test scripts and maintain the tests.
Investment = time needed to construct frameworks and maintenance costs (time to create one test the number of tests)
Source
Maintenance costs also include the costs of identifying analyzing, and resolving the failures of tests. This can include false positives, unstable tests as well as development bugs, and actual failures in tests.
Maintenance costs = time for one test that fails The percentage of failed tests is X percent for each test run amount of test instances X amount of tests
Source
Be aware that frequent failures in tests can make it more difficult and can take longer to reach positive ROI.
Keep in mind that tests are subject to change as time passes. As software grows as the features get added to it, and developers and QA staff may decide to program in more advanced programming languages, and so on. All of this must be included within the return on investment, particularly the costs for maintenance. If a team begins by testing 500 times, it is likely to expand up to 1000 tests (a reasonable estimation) before the time the year's end. If not, something's going off the rails.
Efficiency ROI Calculation:
In this scenario, ROI must be determined in terms of hours. Automated tests can continue for 24 hours while manual testers cannot be expected to be working more than eight hours per day. A lower 24-hour period is 20 or 18 because it's normal to anticipate that the test scenario could be interrupted or paused due to many reasons.
The formula used for Efficiency ROI calculation is:
Automated test script time to develop equals (Hourly automated time for each test * number of test cases that are automated) 8.
Test scripts that are automated for execution duration equal (Automated testing execution times per test of test cases automated * Time period of ROI) 18
Automated analysis time of testis (Test Time for Analysis * ROI Period) * 8
Automated maintenance time for tests is (Maintenance time * Time of ROI) /8
The Manual Execution time (= (Manual Test execution time * the number of manual test cases * Time of ROI) 8
Source
In the formula above the phrase "Period of ROI" is referring to the period (usually weeks) that ROI will be determined. The ROI is then divided into 8 for cases of manual labor and then by 18 or 20 when automation is brought into the equation.
This method of calculation is based on total efficiency, rather than only monetary profits. However, it makes assumptions like a scenario that automated tests have completely replaced manual testing (which isn't the scenario) and also that manual testing only requires one tester (something is almost impossible). This calculation is meant to be an estimate, but not the final estimation.
In addition to the formulas discussed previously, the estimation of the ROI of automated testing should also take into account the following aspects:
Once manual testers have been no longer required to conduct routine tests, they are able to concentrate on more productive tasks including more analysis of the design of tests and development, improvements to tests and test development as well as negative and random tests, and so on.
Automation testing can help increase test coverage. Manual testers should not be expected to perform tests for more than a set number of hours. Like humans, they only function at human speed and are subject to human mistakes. This affects the efficiency and quality of testing. Automation solves these issues and minimizes the damage that an organization could suffer due to these factors.
Advanced ROI Calculation Techniques:
We've also covered the fundamentals. In this article, we'll go over two innovative methods for calculating automated ROI of testing the calculation of efficiency ROI and Risk decrease ROI calculations.
Efficiency ROI Calculation:
In this way, investments have precedence over financial gains. For manual testing, you need to take into account the hours of operation for the tester (usually around eight hours). In contrast, the automation test suite is able to operate all day. Take into consideration external disturbances, such as hardware issues or the unexpected absence of a tester. With this ROI calculation method, the duration that is ROI will be split by the number 18 for automation and divided by 8 for manual labor.
The formula below is the basis for ROI calculation based on this method:
Investment = Test script development automated time, plus automated testing script time Automated analysis of test time automated maintenance time for tests + Time for manual test case execution
Gain = manual test execution (or analysis) time The total number of test cases (automation and manual) * Time period of ROI (or 8).
In this way it is necessary to imagine things such as the following:
Test automation has completely replaced manual testing
One tester is the only one that can be considered for manual testing, etc.
Risk Reduction ROI Calculation:
In this manner, it is necessary to determine the advantages of automation independently. An organization adopts automated testing to expand the testing coverage. We all know that manual testing can cause a lot of undiscovered bugs. One of the most difficult can be postproduction-related bugs. The majority of these bugs indicate poor quality testing. When using the risk reduction method concerns that manual approaches are unable to be addressed are also taken care of. The loss in money that companies suffer in the absence of automation is offset by the benefits of the risk reduction method.
It is possible to calculate the risk reduction ROI using the following formula:
Return on Investment = (Reduction in monetary risk Control of cost) (Reduction in monetary risk - Risk control costs
The risk reduction is calculated using this formula:
Reduced risk Reduction in risk (Rate of annual probability of occurrence) * (Expected loss of money due to one time) * (Reduction in the risk occurrence probabilities after the introduction of the risk control)
Note: This content is originally published on this website: https://medium.com/@govindbqurious/how-to-calculate-roi-for-test-automation-1906a56f088e


Comments
Post a Comment